Tax Invoices Demystified
A Simple Step-by-Step Guide for Entrepreneurs
1. What is a Tax Invoice and Why is It Important?
If you’re a small business owner, freelancer, contractor, or service provider, issuing a tax invoice isn’t just a formality – it’s a critical part of running a compliant and professional business. A tax invoice is a legally required document that acts as proof of a taxable sale, detailing the goods or services provided and the tax charged. Without accurate tax invoices, businesses risk penalties, delays in payments, and even loss of trust among clients.
So, what is a tax invoice, and why should you care? A tax invoice is more than a receipt; it’s a comprehensive document that ensures both you and your client are on the same page about the transaction. It also provides the necessary details for tax reporting, helping you stay in line with tax invoice requirements set by regulatory authorities. By issuing tax invoices correctly, you not only comply with tax laws but also streamline your financial record-keeping, making tax season a lot less stressful.
In this article, we’ll simplify the process of creating a tax invoice, explaining:
1. What a tax invoice is and how it differs from other invoices.
2. The mandatory details every tax invoice must include to meet legal requirements.
3. How to create a tax invoice, with tips and best practices to ensure accuracy and professionalism.
Whether you’re new to issuing tax invoices or want to refine your process, this guide will walk you through everything you need to know, all in plain, easy-to-understand language. Let’s dive in!
2. What Is a Tax Invoice? A Clear Definition and Its Importance
If you’ve ever wondered, “What is a tax invoice?” you’re not alone. Understanding this crucial document is essential for businesses, freelancers, and contractors who need to stay on top of their tax obligations. Let’s break it down in simple terms:
A tax invoice is a formal document issued by a seller to a buyer, detailing the goods or services provided and the applicable taxes, such as VAT (Value Added Tax) or GST (Goods and Services Tax). Unlike a regular invoice, a tax invoice explicitly includes information about the tax charged on the transaction, making it a vital tool for both businesses and tax authorities to track taxable sales.
Tax Invoice Definition: What Sets It Apart?
To fully grasp the concept, let’s compare a tax invoice to a regular invoice:
| Regular Invoice | Tax Invoice |
| Lists details of goods or services sold. | Lists goods or services sold with tax details. |
| Does not require tax-specific information. | Must include tax-specific elements like tax rate, tax amount, and seller’s tax identification number. |
| Often used for non-taxable transactions. | Mandatory for taxable transactions involving VAT or GST. |
In essence, a tax invoice serves two purposes: it acts as proof of a sale and ensures proper documentation for tax reporting.
Legal Requirements: Why Tax Invoices Are Essential
Governments worldwide enforce strict rules around tax invoices to ensure tax compliance and transparency in business transactions. These legal requirements mandate that any taxable business issue a tax invoice for each taxable transaction. Failing to do so can result in hefty penalties, audits, or even legal action.
Key benefits of issuing a compliant tax invoice include:
1. For Businesses: It simplifies record-keeping and ensures accurate tax reporting.
2. For Buyers: It allows them to claim tax credits where applicable (e.g., input tax credits for businesses registered under VAT or GST).
3. For Tax Authorities: It creates an audit trail to track tax liabilities and prevent tax evasion.
What Must Be Included in a Tax Invoice?
A compliant invoice with tax must contain specific details to meet legal standards. These typically include:
1. Business Details: Name, address, and tax registration number of the seller.
2. Customer Details: Name and address of the buyer (in certain cases).
3. Invoice Details: Unique invoice number, issue date, and a description of goods or services.
4. Tax Information: Tax rate, amount of tax charged, and total amount including tax.
5. Additional Notes: If the buyer is eligible for tax credits, the invoice must state this explicitly.
Here’s an example:
> A tax invoice for a graphic designer providing a service might look like this:
> Service provided: Logo design
> Amount: $1,000
> Tax rate: 10% GST
> Tax amount: $100
> Total: $1,100
This level of detail ensures clarity and compliance while making it easier for both parties to manage their tax obligations.
Why Tax Invoices Matter for Businesses
Tax invoices aren’t just a legal requirement – they’re also a cornerstone of good financial management. Issuing accurate tax invoices helps businesses:
- Maintain a clear record of taxable sales.
- Avoid disputes with clients over incorrect tax charges.
- Claim input tax credits (for eligible businesses).
- Present a professional image, which builds trust with clients and partners.
At the same time, tax authorities benefit from tax invoices as they provide a transparent and standardized way to monitor tax collection.
Tax Invoice Explained in Simple Terms
To summarize, a tax invoice is much more than a bill – it’s a document that protects both businesses and buyers by ensuring tax-related transparency. By including key tax details and adhering to legal requirements, it serves as proof of compliance and helps streamline tax reporting.
Whether you’re running a small business or freelancing, issuing proper tax invoices is a must. Now that you know the tax invoice definition and its significance, you can confidently issue invoices that meet both client expectations and legal standards.
3. What Details Should a Tax Invoice Include? A Guide to Essential Components
Creating a tax invoice might seem straightforward, but there are important components that must be included for it to be legally valid and tax-compliant. Whether you’re a small business owner, freelancer, contractor, or service provider, understanding the tax invoice components is key to ensuring that your invoices meet legal standards and help maintain smooth business operations.
In this guide, we’ll break down the essential elements that must appear in every tax invoice. We’ll also look at how different tax systems, such as VAT or GST, can affect the information you need to include. Let’s dive in!
1. Seller’s Details: Who Are You?
The first crucial component of any tax invoice is the seller’s information. This section confirms your identity as the provider of the goods or services, and it helps your customer know who they are transacting with.
Essential details for the seller include:
- Business Name: The official name of your business or your trading name.
- Address: Your registered business address. This is especially important if you operate from a physical location, but even home-based businesses must include this.
- Contact Information: Include a phone number or email address where clients can reach you for questions about the invoice.
- Tax Registration Number (ABN, VAT number, or equivalent): This is crucial for tax compliance. For example, in countries like Australia, a seller must include their Australian Business Number (ABN). For VAT, you may need a VAT registration number.
2. Buyer’s Details: Who Are They?
Next, the tax invoice should clearly state the buyer’s details. These help identify the customer and ensure that the transaction is correctly documented for tax purposes.
Buyer information typically includes:
- Name or Business Name: The name of the individual or company purchasing the goods or services.
- Address and Contact Info: While not always mandatory, some tax systems may require you to list the buyer’s address and contact details.
In cases where businesses or companies are the buyer, ensure that their official name is listed correctly and include the business registration number if necessary.
3. Unique Invoice Number: No Two Are the Same
Every tax invoice must have a unique number. This is crucial for record-keeping, auditing, and avoiding confusion with other invoices. The invoice number should follow a sequential format (e.g., INV-001, INV-002) and not be reused.
Why is this important?
- It helps both you and your client track payments.
- It ensures that your invoices are organized for tax reporting purposes.
- It avoids errors during audits and financial reviews.
For best practices, try to develop a numbering system that works for your business, such as including a year (e.g., 2024-001) to help you keep track of invoices over time.
4. Invoice Date: When Was It Issued?
The date the invoice is issued is essential for both legal and financial purposes. It marks the official start of the payment period and indicates when the transaction took place.
Ensure you clearly state:
- Invoice Date: The day the invoice was created and sent to the customer. This date is important because payment terms are often calculated from it.
5. Description of Goods or Services: What’s Being Sold?
One of the most important components of a tax invoice is a clear and detailed description of the goods or services provided. This helps ensure there is no confusion or disagreement about what is being charged for.
Include:
- Clear Breakdown of Goods/Services: Each item or service should be listed separately, with a brief description. For example, instead of just “Consulting Services,” you might specify “Marketing Consultation (5 hours)” to provide more clarity.
The more transparent and specific the description, the fewer the chances for disputes or misunderstandings.
6. Quantity and Price: How Much Are You Charging?
This is where you’ll list the quantity of the goods sold or the number of hours worked and the corresponding price per unit or rate.
For example:
- Quantity: If selling products, specify how many units the customer is purchasing. If providing services, list the number of hours worked.
- Price: Clearly state the price per unit (e.g., $50 per hour or $200 per product).
This section helps the buyer understand how the total was calculated.
7. Tax Amount: What’s the Tax?
A key difference between a regular invoice and a tax invoice is the inclusion of tax details. A tax invoice must clearly outline the tax rate and the amount of tax charged. The tax amount should be calculated based on the price of goods or services before tax.
For example:
- Tax Rate: Specify the tax rate applied, such as 10% GST or 20% VAT.
- Tax Amount: If the price before tax is $500, a 10% tax rate would charge $50 in tax.
Including the tax amount is critical for your business to ensure tax compliance and for your client to claim any available tax credits.
8. Total Amount Due: How Much Do They Owe?
This is the final section of the invoice, which sums up the total amount that the buyer needs to pay. It should include the cost of the goods or services, the tax charged, and any additional fees.
For example:
Subtotal: Price before tax.
Tax Amount: The tax added to the price.
Total Amount Due: Subtotal plus tax.
Always ensure this section is clear and easy to understand, as it’s where the buyer will look to confirm the payment they owe.
9. Payment Terms: How and When to Pay
This section outlines the terms under which payment should be made. It may include:
Payment Due Date: Specify when payment is expected (e.g., within 30 days).
Late Fees: If you charge interest for late payments, include this information.
Payment Methods: Indicate the payment methods you accept (e.g., bank transfer, credit card, PayPal).
Variations for Different Tax Systems: VAT vs. GST
Depending on where you are located, the type of tax you apply to your invoices will differ. In some countries, businesses must charge VAT (Value Added Tax), while in others, GST (Goods and Services Tax) is more common.
For instance:
VAT invoices may need to include the VAT number of both the seller and buyer, depending on local tax laws.
GST invoices often follow similar requirements, but the tax rates may vary by country or region.
Sample Tax Invoice
Here’s an example of a tax invoice format that includes all the required components:
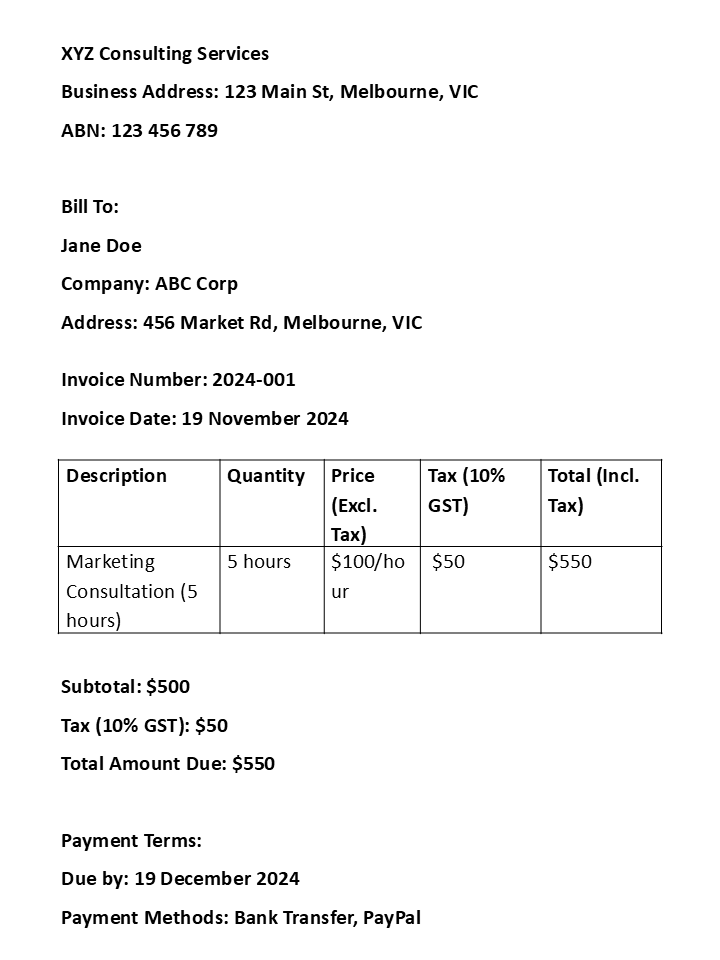
A tax invoice is not just a document for requesting payment; it’s a critical tool for businesses to comply with tax regulations. By including all the tax invoice details listed above, you ensure both legal compliance and smooth business operations. With a clear understanding of what to include in a tax invoice, you’ll avoid errors and help your customers process payments more efficiently.
4. How to Make a Tax Invoice: A Step-by-Step Guide
Creating a tax invoice doesn’t have to be complicated, but it’s essential to ensure that it includes all the necessary details to meet legal requirements. Whether you’re new to invoicing or looking to streamline the process, this step-by-step guide will walk you through how to make a tax invoice efficiently, whether manually, using an invoicing template, or with invoicing software.
1. Choose Your Invoicing Method: Manual or Software?
The first decision you need to make is how to create your tax invoice. There are several methods, each with its own benefits:
- Manual Method (Word or Excel):
- For those who prefer a DIY approach, creating a tax invoice using programs like Word or Excel is a simple and free option. You can either create your invoice from scratch or use a pre-designed template that you fill out manually.
- Invoice Template:
- Many businesses opt to use an invoice template for consistency and ease. You can find templates online or within software like Word or Excel that are designed specifically to help you create a tax invoice format. Templates are particularly helpful because they guide you through the necessary components of a tax invoice.
- Invoicing Software:
If you’re looking to automate the process, invoicing software is a great option. Tools like QuickBooks, Vantazo, or Xero not only allow you to create tax invoices easily but also help track payments and manage your finances in one place. Software usually offers tax-specific templates, ensuring compliance with tax regulations.
2. Gather the Necessary Information
Before creating the invoice, it’s important to collect all the relevant details to include. This ensures your tax invoice is complete and accurate. Here’s what you’ll need:
- Client’s Contact Information:
This includes the client’s name, business name (if applicable), and their address or contact details. You may also need the client’s tax registration number if they are a business that is VAT/GST registered.
- Description of Goods or Services:
Clearly list each product or service you are charging for, including the quantity, unit price, and any other specific details that are relevant to the transaction.
- Tax Rate:
You need to know the correct tax rate (such as VAT, GST, etc.) to apply to the sale. This may vary based on your location and the nature of your products or services.
3. Fill in the Tax-Specific Details
Once you’ve gathered all the necessary information, it’s time to fill in the tax-specific details:
- Tax Amount:
Ensure that the tax rate is clearly stated (e.g., 10% VAT or 5% GST). Apply this rate to the total price before tax to calculate the tax amount.
- Tax Identification Number:
Include your tax registration number (e.g., ABN, VAT ID) as required by law. If you are in a country with VAT/GST, this is an essential part of the invoice. Some countries also require the buyer’s tax identification number for B2B transactions.
- Total Amount Due:
The final amount should include the subtotal (price before tax), the tax amount, and the total amount due (price including tax). Make sure the amounts are easy to read and clearly stated.
4. Check Compliance with Tax Regulations
Once your invoice is filled out, verify that it complies with the tax invoice requirements in your country or region. Every country has specific tax laws, and failing to meet the necessary criteria could result in penalties. Ensure the following:
- Correct Tax Rate:
Double-check that the tax rate (e.g., VAT, GST) applied is accurate based on the location and nature of your business.
- Legal Details:
Ensure your tax registration number is included, and your invoice follows any specific format or layout required by the local tax authority. For instance, in countries with VAT systems, certain items may need to be itemized differently.
- Invoice Numbering:
As mentioned earlier, make sure your invoice number is unique and sequential, which is a legal requirement in most tax systems.
5. Send the Invoice
Once your tax invoice is complete, it’s time to send it to your client. The method of delivery can vary based on your and your client’s preferences, but here are the most common options:
- Digital Invoices (Email or Online Platforms):
Digital invoices are fast and convenient. You can email the tax invoice directly to your client or send it through online invoicing platforms like QuickBooks, Vantazo, or Xero. These platforms allow you to generate the invoice with just a few clicks and send it securely.
- Hard Copy:
If your client prefers paper invoices, you can print and mail the invoice. Keep in mind that this may take longer and involve additional costs, such as postage.
- Invoice Follow-Up:
If payment isn’t received within the agreed timeframe, send a polite follow-up to remind the client of the outstanding amount. Some invoicing software automatically sends reminders for you.
Tools and Software to Simplify Tax Invoice Creation
While you can manually create a tax invoice using Word or Excel, using invoicing software can save you time and help ensure compliance with tax laws. Here are a few tools that can make the process smoother:
QuickBooks:
QuickBooks allows you to create custom tax invoices, track payments, and even automatically calculate taxes for you based on the region you’re in. It’s particularly useful for businesses that need a comprehensive accounting tool.
Vantazo:
Vantazo is a user-friendly invoicing software that’s designed specifically for small businesses and freelancers. It allows you to create tax invoices, track billable hours, and manage payments—all in one platform.
Xero:
Xero is another powerful tool for managing invoicing, accounting, and tax compliance. It offers customizable tax invoice templates, automatic tax calculations, and integration with other financial tools.
If you’re looking to make the process even easier, using invoicing software like QuickBooks, Vantazo, or Xero can help automate the process, saving you time and reducing the chance of errors. Whether you do it manually or use a tool, knowing how to make a tax invoice will streamline your business operations and ensure you stay on top of your tax obligations.
5. What Is a Recipient-Created Tax Invoice?
A Recipient-Created Tax Invoice (RCTI) is an alternative to the traditional tax invoice, where the buyer (recipient of goods or services) creates the invoice instead of the supplier. This system is particularly used in specific industries or transactions, usually when both parties are registered for GST or similar tax schemes.
When Are RCTIs Used?
RCTIs are most commonly used in industries where there is a need for greater flexibility or simplicity in invoicing. They are typically applied in business-to-business (B2B) transactions between GST-registered entities, particularly in sectors like construction or agriculture.
Some scenarios where RCTIs are used include:
Construction Contracts: In the Australian construction industry, RCTIs are often used in contracts where contractors are working on behalf of a principal contractor. The recipient (usually the contractor) creates the invoice for the goods or services provided.
Supply of Agricultural Goods: In certain agricultural supplies, such as between farmers and wholesalers, an RCTI may be used when both parties are GST-registered.
To be eligible to issue an RCTI, both the buyer and seller must agree to the arrangement, and it’s important that the buyer adheres to the necessary compliance rules set out by the tax authority in their jurisdiction.
Advantages of RCTIs
1. Streamlined Process for Recipients:
The buyer creates the invoice, making it easier for them to keep track of their GST liabilities and reduce administrative overhead on the supplier’s side.
2. Flexibility in Timing:
In some cases, the buyer may have more control over the invoicing process, allowing for more accurate timing in terms of tax reporting and claiming GST credits.
3. Simplifies Complex Transactions:
In industries like construction, where multiple subcontractors and suppliers are involved, RCTIs help streamline complex invoicing scenarios, ensuring that tax obligations are met efficiently.
—
Challenges of Using RCTIs
While RCTIs offer certain benefits, there are also potential drawbacks:
Risk of Errors: Since the buyer is responsible for creating the invoice, there’s a risk of incorrect or incomplete tax details, which could lead to penalties.
Compliance Requirements: Both parties must ensure they comply with the RCTI rules to avoid any issues with tax authorities. If the tax office audits the transaction, both the buyer and seller need to ensure that their arrangements are documented properly.
Example of an RCTI Scenario
In a construction contract, a subcontractor may perform work on a project, and the principal contractor (the recipient) may issue an RCTI for the work completed. This is especially common in industries where multiple small contracts are handled, and the recipient is better positioned to track the GST.
A Recipient-Created Tax Invoice (RCTI) is an invoicing method that allows the buyer, rather than the supplier, to create the invoice for goods or services. It’s used mainly in B2B transactions between GST-registered entities in industries like construction. While it offers flexibility and efficiency, both parties must be aware of the associated compliance rules to avoid errors and ensure proper tax reporting.
6. What Is a Tax Invoice Used For?
A tax invoice is a crucial document for businesses, serving several important purposes related to financial record-keeping, tax reporting, and transaction verification. It helps businesses stay compliant with tax laws and is used to track transactions involving goods and services. Here’s how a tax invoice is used:
1. Record-Keeping
One of the primary purposes of a tax invoice is to serve as an official record of a business’s sales and purchases. By issuing and receiving tax invoices, businesses can maintain accurate records of their transactions. This helps businesses keep track of their income and expenses, which is essential for financial reporting, auditing, and managing cash flow.
For example, a retail store issues tax invoices to customers for every sale, helping them keep track of sales revenue.
Similarly, businesses receiving goods or services from suppliers will keep the tax invoices as records of their purchases.
2. Tax Reporting
A tax invoice is required for businesses to report taxes to tax authorities. This includes submitting tax returns and paying taxes owed, such as VAT or GST. The tax invoice ensures businesses accurately calculate their tax liabilities by documenting the tax amount included in each transaction.
For example, at the end of the tax period, a business will review all the tax invoices it has issued and received to determine how much tax it owes or how much tax it can claim back. Accurate reporting ensures compliance with tax laws and prevents penalties for underreporting taxes.
3. Proof of Transaction
A tax invoice also serves as legal proof of a transaction between a seller and a buyer. It outlines the goods or services sold, the agreed-upon price, and the tax charged. This can be crucial if there’s any dispute or need for clarification about the transaction.
For instance, if a customer disputes a charge, the tax invoice acts as documentation to support the transaction details, such as the amount, the items purchased, and the applicable taxes.
4. Claiming Tax Credits
Tax invoices are necessary for claiming tax credits (like VAT or GST credits) on purchases made. Businesses can use tax invoices to claim back the tax paid on business-related expenses. This helps reduce the overall tax burden, ensuring that businesses only pay tax on the value they add.
For example, a business that buys office supplies from a supplier will receive a tax invoice showing the amount of GST paid. When filing their taxes, the business can use this tax invoice to claim back the GST, reducing their tax liability.
Example of Tax Invoice Use
Let’s say a freelance graphic designer purchases design software for their business. The software company issues a tax invoice showing the price of the software and the GST paid. When filing their GST return, the designer uses this tax invoice to claim the GST as a credit, reducing the amount of tax they owe.
A tax invoice serves multiple purposes in business operations: record-keeping, tax reporting, proof of transaction, and claiming tax credits. By ensuring all the necessary details are included, businesses can stay compliant with tax laws, manage their finances efficiently, and reduce tax liabilities.
7. Best Practices for Tax Invoices
Creating and managing tax invoices efficiently is essential for staying compliant with tax laws and maintaining smooth business operations. By following best practices for tax invoices, businesses can avoid mistakes, reduce delays, and ensure that they meet all legal and tax requirements. Here are some best practices to keep in mind when creating and managing tax invoices:
1. Accuracy
One of the most important best practices is ensuring the accuracy of the information on the tax invoice. Small errors in details like the tax rate, client name, or invoice number can lead to disputes, delays, and even tax compliance issues. Always double-check the tax amount, description of goods or services, and payment terms. Accurate invoices prevent unnecessary back-and-forth with clients and ensure the correct amount of tax is charged.
2. Timeliness
Issue tax invoices promptly after the delivery of goods or services. Timely invoicing ensures that the payment process begins without unnecessary delays, which is crucial for maintaining cash flow. In many cases, businesses are required by law to issue a tax invoice within a certain time frame, so adhering to this practice can help avoid penalties and interest charges for late submissions.
3. Clarity
The tax invoice should be clear and easy to understand. Key details like the tax amount, description of the goods or services provided, and the total amount due should be prominently displayed. A well-organized invoice reduces confusion and the likelihood of disputes, making it easier for the buyer to understand what they are paying for and how much tax is included.
For example, clearly highlight the subtotal (before tax), the tax amount, and the total (after tax).
4. Compliance
Stay up-to-date with the latest tax regulations to ensure your invoices meet all the legal requirements of your country or region. Tax laws can change, and failing to comply with them can lead to penalties or complications. Make sure your tax invoice includes the necessary details, such as your business’s tax registration number, the applicable tax rate, and the correct format.
5. Record-Keeping
It’s crucial to keep a copy of every tax invoice issued. Whether you store them digitally or in physical form, proper record-keeping ensures you have access to historical invoices when needed for accounting, audits, or tax returns. Proper records also help you claim back tax credits and track your income and expenses.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
1. Incorrect Tax Rates:
Applying the wrong tax rate (e.g., using 10% instead of 5% GST) can lead to overcharging or undercharging, both of which can cause issues with tax authorities.
2. Missing Client Details:
Failing to include the buyer’s name, contact information, or tax ID (if required) can make the invoice invalid and may lead to non-compliance.
3. No Unique Invoice Number:
Every tax invoice must have a unique number for proper tracking and compliance. Missing or duplicate invoice numbers can lead to confusion or tax issues.
By following these best practices for creating and managing tax invoices, businesses can ensure accuracy, timeliness, and compliance, avoiding common mistakes and fostering smooth financial operations. Whether you’re invoicing for a small business or a larger company, proper tax invoice management is key to staying organized and meeting your tax obligations.
8. Conclusion
In summary, a tax invoice is a vital document for any business, as it ensures tax compliance and provides a clear record of transactions. It must include specific details such as the tax rate, descriptions of the goods or services, and the seller and buyer information. Properly issued tax invoices help businesses maintain accurate records, fulfill tax reporting obligations, and ensure that tax credits can be claimed when applicable.
To streamline the process and ensure compliance, businesses should consider using invoicing software or templates. These tools can help create professional tax invoices quickly, ensuring that all necessary information is included and the format meets legal requirements. This can save time, reduce errors, and avoid potential issues with tax authorities.
By following the best practices outlined in this guide, you can ensure that your tax invoices are both compliant and professional, contributing to smooth financial operations and successful business growth.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. Can I issue a tax invoice if I’m not registered for VAT?
No, you cannot issue a tax invoice if you are not registered for VAT or any other applicable tax. Tax invoices can only be issued by businesses that are registered for VAT or similar taxes. If you’re not registered, you should issue a regular invoice without tax details.
2. What happens if I forget to include tax on my invoice?
If you forget to include the correct tax amount on your tax invoice, you may face compliance issues with tax authorities. It could lead to underreporting your tax obligations, resulting in penalties or fines. It’s important to double-check that all tax details are correctly included before sending the invoice.
3. Do I need to issue a tax invoice for every sale?
Generally, a tax invoice is required for sales between businesses or for any taxable transactions with customers who are registered for VAT or similar taxes. However, some small transactions may not require a tax invoice, depending on local tax regulations. Always check your local tax rules to ensure you’re compliant.
4. Can a tax invoice be issued electronically?
Yes, tax invoices can be issued electronically as long as they meet all legal requirements and include all necessary details. Electronic invoices are commonly used in modern businesses, and many invoicing software tools support the creation and sending of tax invoices electronically.



