Say Goodbye to Paper Cuts
How EDI 810 Invoices Are Revolutionizing Billing
Introduction
In today’s fast-paced business world, efficiency is everything. That’s where Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) comes in. EDI is like the unsung hero of modern business transactions – working quietly behind the scenes to make things run smoothly. Imagine sending an invoice without ever touching a piece of paper, or manually typing in a number. Sounds too good to be true, right? Well, it’s not! EDI makes it possible, and one of the key players in this digital revolution is the EDI 810 invoice.
So, what exactly is EDI, and why should you care? Simply put, EDI is the electronic exchange of business documents between organizations in a standardized format. This eliminates the need for paper, manual entry, and, let’s face it, human error. And the EDI 810 invoice? It’s the digital version of the traditional invoice, but with a twist – it’s faster, more accurate, and way more efficient.
When you implement EDI invoicing, you’re not just saving time. You’re also reducing costs, improving accuracy, and speeding up your cash flow. It’s like trading in your old, clunky phone for a shiny new smartphone. The benefits of EDI invoicing are clear, and businesses everywhere are hopping on the bandwagon. So, let’s dive in and explore how the EDI 810 invoice can transform your billing process.
1. What Is an EDI 810 Invoice?
In today’s fast-paced world of business, invoicing has evolved beyond the traditional paper-based methods. Enter the EDI 810 invoice, a game-changer in the world of billing. But what exactly is it? Simply put, an EDI 810 invoice is a standardized electronic invoice format used to exchange billing information between trading partners through Electronic Data Interchange (EDI) systems. This format allows businesses to send and receive invoices digitally, making the invoicing process faster, more accurate, and less prone to errors.
- The Role of EDI 810 Invoices in the Bigger Picture
EDI is a framework that allows businesses to electronically exchange documents like orders, invoices, and shipping notices in a standardized format. The EDI 810 invoice is one of the key documents in this framework, specifically used for billing. Its role is critical in industries that rely on fast and efficient B2B transactions, like manufacturing, retail, and logistics. In this system, when a seller completes a transaction, they generate an EDI 810 invoice and send it electronically to the buyer, typically through a secure EDI network. The buyer then processes the invoice directly into their system for payment, with minimal human intervention.
- How EDI 810 Differs from Traditional Paper Invoices
When you think of invoices, you probably picture stacks of paper, pens, and possibly a few missed payments. This is where the EDI 810 invoice comes in, offering a modern alternative to traditional paper invoices. Unlike paper invoices that require manual entry and handling, EDI invoices are automated. Data flows directly between systems, reducing the chances of mistakes such as typos or miscalculations. No more lost invoices, no more delays in processing – just a smooth, automated process that saves both time and money.
For example, imagine a manufacturing company sending hundreds of invoices to different clients every month. Using EDI 810 invoices, the company can send electronic invoices to all their customers with just a few clicks, cutting down on paper use, reducing the cost of mailing, and ensuring faster payment processing.
The EDI 810 Invoice in Action
The EDI 810 invoice is widely used across various industries. In retail, it’s used for transactions between wholesalers and retailers to ensure accurate and timely billing. In manufacturing, it streamlines the exchange of invoices between suppliers and manufacturers, making the supply chain more efficient. Similarly, logistics companies use EDI invoicing to send shipping invoices electronically, allowing for faster reconciliation of goods delivered.
Let’s consider a real-world example: A retailer places a bulk order with a supplier for new stock. Once the goods are shipped, the supplier generates an EDI 810 invoice and sends it electronically to the retailer. The retailer receives the invoice directly in their accounting system, where it’s automatically recorded and matched to the original purchase order and shipment. This seamless flow of information speeds up the entire process, from order to payment.
Why Should Businesses Care About EDI 810 Invoices?
For any business looking to optimize operations and reduce the overhead of manual billing processes, EDI 810 invoices are a no-brainer. They speed up billing, eliminate the paper trail, and reduce the risk of human error. They also make it easier to track payments, handle disputes, and maintain an organized record of transactions, all without piles of paper cluttering up your office.
2. How Does EDI Invoice Work?
EDI invoicing is a game-changer for businesses looking to streamline their billing processes. Rather than relying on paper invoices or manual data entry, EDI allows companies to send and receive invoices electronically, in a standardized format. So, how exactly does the EDI invoicing process work? Let’s break it down, step-by-step, to make things crystal clear.
1. Generation of the Invoice by the Seller’s System
The process begins when a seller generates an invoice. Instead of creating a traditional paper invoice, the seller’s accounting system automatically creates an EDI 810 invoice in a standardized electronic format. This format adheres to specific EDI standards, like ANSI X12, which ensures that the information is structured in a way that can be easily understood by any computer system.
The invoice generated typically includes all the relevant details: the amount due, the products or services provided, payment terms, and more. This is all done automatically within the seller’s software, saving time and reducing the chances of human error.
2. Transmission of the Invoice via Secure EDI Networks
Once the invoice is ready, it is transmitted electronically from the seller’s system to the buyer’s system through a secure EDI network. There are various ways this communication happens, often through Value-Added Networks (VANs) or over the internet via secure protocols like AS2 (Applicability Statement 2), FTP (File Transfer Protocol), or SFTP (Secure File Transfer Protocol). These secure networks ensure that the invoice is safely delivered and cannot be intercepted by unauthorized parties. Think of it as sending a digital envelope that only the intended recipient can open.
3. Receipt and Processing of the Invoice by the Buyer’s Accounting System
Once the invoice reaches the buyer, the next step is processing. The buyer’s accounting system receives the EDI 810 invoice and automatically reads the data. The beauty of EDI invoicing is that the buyer’s system can instantly recognize the information and match it with the purchase order or delivery receipt.
For example, let’s say a retailer receives an EDI invoice for a batch of goods from a supplier. The buyer’s system checks the details of the invoice against the original order to ensure everything matches up. If the invoice is correct, it’s automatically approved for payment. If there are discrepancies, the system flags it for manual review. This reduces the time spent on manual checks and ensures faster, more accurate processing.
Once everything checks out, the payment is processed, and the transaction is complete.
- The Technology Behind EDI Invoices
Behind the scenes, EDI invoicing is powered by complex technology. EDI standards like ANSI X12 (commonly used in North America) and EDIFACT (used globally) define the structure of the electronic invoices, ensuring consistency across different industries and regions. These standards dictate how the data should be organized and formatted, making it possible for various software systems to interpret the same data accurately.
Communication protocols like AS2 and SFTP provide a secure method for transmitting the invoice between businesses. These protocols ensure that the information travels safely over the internet or private networks, with encryption and authentication measures in place to protect sensitive data.
- Real-Life Example: How EDI Saves Time and Reduces Errors
Let’s take a quick look at how EDI invoicing can save time and reduce errors. Imagine a large retailer, like Walmart, receiving invoices from hundreds of suppliers. Without EDI, the company would have to manually process thousands of paper invoices every month. This would mean a lot of time spent checking details, entering data, and waiting for payments to clear.
With EDI invoicing, all invoices are automatically generated, transmitted, and processed without human intervention. This means fewer errors, faster payments, and fewer bottlenecks. For the supplier, they get paid faster, and for the retailer, they can focus on more strategic tasks instead of manually handling invoices.
- Visual Diagram: The EDI Invoicing Workflow
Here’s a simplified diagram to illustrate how EDI invoicing works:
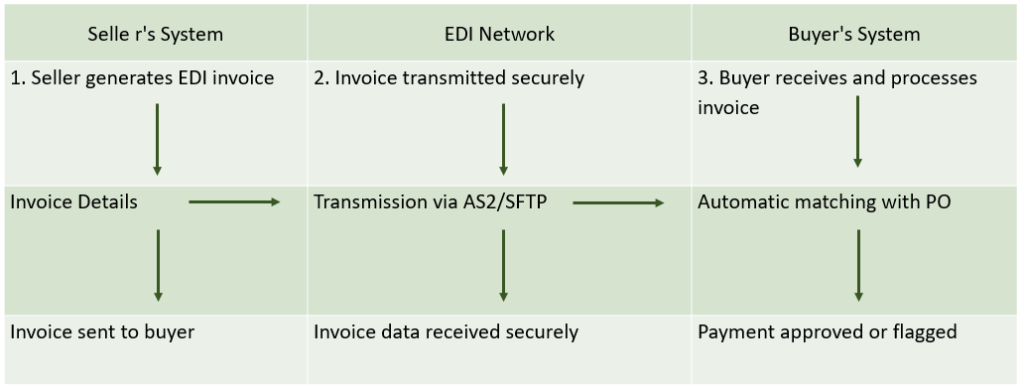
The EDI invoicing process is a perfect example of how technology can improve business efficiency. By eliminating manual processes and reducing errors, EDI invoicing helps companies save time, cut costs, and streamline their operations. From the automatic generation of invoices to their secure transmission and fast processing, EDI invoicing is a win-win for businesses of all sizes.
3. Essential Components of an EDI Invoice
The EDI 810 invoice is designed to automate and streamline the billing process, making invoicing faster and more accurate. But what exactly is included in an EDI invoice? It’s not just a random collection of data – it’s a highly structured document with key components that ensure everything runs smoothly. Let’s break down the essential components of an EDI 810 invoice and understand their significance in facilitating efficient and accurate invoicing.
1. Invoice Number
The invoice number is one of the most critical elements of any invoice. It serves as a unique identifier for the invoice, making it easy for both the seller and the buyer to track and reference. In an EDI 810 invoice, this number is automatically generated by the seller’s system and inserted into the document.
- Significance:
The invoice number ensures there’s no confusion about which invoice is being referenced and helps with record-keeping for both parties. It’s also vital for reconciliation purposes when matching invoices with payments.
- Example:

2. Buyer and Seller Information
The buyer and seller information section includes the names, addresses, and contact details for both the seller and the buyer. This is vital to ensure that the invoice is correctly addressed and that the parties involved can be easily reached if there are any issues.
- Significance:
Correct buyer and seller information reduces the risk of errors, such as sending the invoice to the wrong address or contacting the wrong person for payment. It also helps in managing communication between trading partners.
- Example:
Buyer: XYZ Retailer Address: 123 Market St, Suite 101, Cityville, ST 45678 Phone: (123) 456-7890 Seller: ABC Supplier Address: 987 Industrial Rd, Cityville, ST 98765 Phone: (987) 654-3210 |
In the EDI 810 invoice, this would be automatically inserted into the correct fields based on the established trading relationship.
3. Item Details (Descriptions, Quantities, Prices)
This section provides a detailed breakdown of the products or services being billed. It typically includes the following information:
– Item descriptions: Clear, concise descriptions of the goods or services.
– Quantities: The number of units of each item.
– Prices: The price per unit or service and the total amount for each item.
- Significance:
The item details ensure that both parties are clear on what is being billed. This component prevents misunderstandings about quantities, pricing, and the scope of the sale.
- Example:
| Item: Blue Widget Quantity: 10 Price: $50.00 each Total: $500.00 Item: Red Gadget Quantity: 5 Price: $30.00 each Total: $150.00 |
In an EDI 810 invoice, the item information will be formatted according to EDI standards, making it easy for the buyer to verify and match the order.
4. Payment Terms
The payment terms section outlines how and when the payment for the invoice should be made. This may include:
– Due date: The exact date by which the invoice should be paid.
– Discounts: If the buyer can receive a discount for early payment (e.g., 2% discount if paid within 10 days).
– Payment method: The preferred method of payment (e.g., bank transfer, credit card).
- Significance:
Clear payment terms help avoid payment delays and confusion. This section sets expectations for when the buyer must pay and may incentivize quicker payment with discounts.
- Example:
Payment Terms: Net 30 (Payment due 30 days from invoice date)
Early Payment Discount: 2% if paid within 10 days
In the EDI 810 invoice, these terms are automatically included, ensuring both parties are aligned.
5. Total Amount Due
The total amount due is the final value that the buyer needs to pay. This includes the sum of all items, taxes, discounts, and any additional fees. It’s typically the last field on the invoice, clearly marking the amount owed.
- Significance:
The total amount due is the key figure that dictates the payment transaction. This field ensures there’s no ambiguity regarding the final amount, reducing the risk of disputes.
- Example:
| Subtotal: $650.00 Sales Tax (5%): $32.50 Discount: -$13.00 Total Amount Due: $669.50 |
In an EDI 810 invoice, the total is automatically calculated and included in the appropriate section.
6. Additional Components
While the components above are the core elements of an EDI 810 invoice, some invoices may also include additional information, such as:
– Purchase order number: This helps match the invoice to the original purchase order.
– Ship-to address: The address where the goods should be delivered.
– Invoice date: The date the invoice was created, which also helps with tracking payment deadlines.
- Customizing Your EDI Invoice
One of the advantages of EDI invoicing is its flexibility. While certain components are standard, businesses can tailor their EDI invoices to meet their specific needs. For instance:
– You can add custom fields for specific order or project numbers.
– You can include more detailed descriptions or even notes for special payment instructions.
– You can adjust the layout to reflect your brand’s look and feel, even though the underlying data remains in a standardized format.
It’s essential to work with your EDI software provider or trading partners to ensure the customizations align with your business requirements without causing confusion or errors in the transaction process.
4. Benefits of Using EDI Invoice
In today’s digital world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve efficiency and streamline their operations. One area where significant gains can be made is invoicing. The EDI 810 invoice, a standardized electronic invoice format, offers numerous advantages over traditional paper invoicing. From faster processing times to cost savings, adopting EDI invoicing can help businesses of all sizes modernize their billing processes. Let’s explore the key benefits of using EDI invoices and how they can transform your operations.
1. Increased Efficiency and Speed in Processing Invoices
One of the biggest benefits of EDI invoicing is the speed at which invoices are processed. Traditional paper invoices require manual handling, whether that means printing, mailing, or scanning. With EDI, invoices are sent electronically, eliminating delays from postal services or manual data entry.
For example, when a supplier sends an EDI 810 invoice, the buyer’s system can automatically read and process the data, matching it with the original purchase order. This automation significantly speeds up the invoicing cycle. The invoice is approved for payment almost immediately, allowing the buyer to pay faster and the seller to receive payment quicker.
- Use Case:
A retail chain that switched to EDI invoicing reported a 30% reduction in the time it took to process invoices, leading to faster payments and improved cash flow. The company was able to approve invoices in real-time, eliminating the back-and-forth delays often seen in traditional invoicing systems.
2. Reduction in Errors and Discrepancies
Manual data entry is prone to human error, whether it’s a typo, a missed digit, or an incorrect total. These errors can lead to discrepancies, delayed payments, and strained business relationships. EDI invoicing helps eliminate these mistakes by automating the process.
The EDI 810 invoice follows a standardized format that’s automatically read and processed by the buyer’s system. This reduces the risk of errors, such as incorrect invoice amounts or mismatched product descriptions. Even when discrepancies do occur, they are easily flagged by the system, making it easier to resolve quickly.
- Use Case:
A manufacturer using EDI invoicing for its billing process found a significant drop in invoice disputes. Before switching to EDI, the company faced an average of 10% of invoices being disputed due to human error. After implementing EDI invoicing, disputes dropped to less than 1%, thanks to automated data entry and validation.
3. Cost Savings from Eliminating Paper and Manual Processes
The environmental and financial costs of paper invoicing can quickly add up. Printing, mailing, and storing paper invoices is not only time-consuming but also expensive. On the other hand, EDI invoicing eliminates the need for paper, ink, postage, and physical storage space.
By adopting EDI invoicing, businesses save money on materials and resources, while also reducing the labor involved in processing and filing invoices. These savings can be reinvested into other areas of the business, allowing companies to operate more cost-effectively.
- Use Case:
A wholesale distributor transitioned from paper-based invoicing to EDI invoicing and saw immediate cost savings. The company saved $50,000 annually by eliminating paper invoices, postage, and storage costs. Additionally, the automation of the invoicing process reduced the need for manual labor, further contributing to cost reductions.
4. Enhanced Tracking and Reporting Capabilities
EDI invoicing offers businesses better tracking and reporting capabilities. Since the entire invoicing process is digital, all invoice data is stored in electronic systems that can be easily accessed and analyzed. Companies can generate reports to track payments, monitor invoice statuses, and identify trends or issues in their billing processes.
For instance, businesses can quickly generate reports showing outstanding invoices, payment history, and the average time it takes to receive payment. This level of visibility helps businesses make more informed decisions and take action to improve cash flow and reduce outstanding debt.
- Use Case:
A logistics company implemented EDI invoicing and used the enhanced reporting features to identify patterns in payment delays from certain customers. Armed with this information, the company was able to take proactive steps, such as sending payment reminders, resulting in a 25% improvement in on-time payments.
5. Improved Relationships with Trading Partners
Switching to EDI invoicing can significantly improve relationships with trading partners. The speed, accuracy, and transparency that come with automated invoicing make it easier for both parties to trust that the transaction details are correct and payments will be processed efficiently. By adopting EDI invoicing, businesses can improve the reliability of their billing process, leading to better relationships with suppliers, customers, and other trading partners. In today’s fast-paced business environment, this type of efficiency can give you a competitive edge.
- Use Case:
A major electronics supplier started using EDI invoices for all transactions with its partners and saw a noticeable improvement in partner satisfaction. With fewer errors and faster payment cycles, the supplier gained a reputation for being easy to work with, which strengthened their relationships and led to more favorable terms with their trading partners.
- Why Use EDI Invoicing?
The benefits of EDI invoices are clear: faster processing, fewer errors, significant cost savings, better tracking, and improved relationships with trading partners. By switching to EDI 810 invoices, businesses can modernize their invoicing systems, reducing manual workload and enhancing the overall efficiency of their financial operations.
If you’re still using paper-based invoicing or manually entering data, it’s time to consider EDI invoicing as a way to streamline your processes, reduce costs, and improve cash flow. In a world that’s increasingly focused on automation and speed, EDI invoicing is the future—and it’s already here.
5. How Do I Create an Invoice With EDI?
Setting up and creating EDI invoices might seem like a complex process at first, but once you break it down into manageable steps, it becomes much easier. EDI invoicing automates and streamlines your invoicing process, saving you time, reducing errors, and improving efficiency. Here’s a step-by-step guide to help you set up and create EDI invoices, from selecting the right software to troubleshooting common issues.
1. Choosing an EDI Solution Provider
The first step in creating EDI invoices is selecting an EDI solution provider. There are many EDI platforms available that offer various features, including invoice creation, document transmission, and secure communication. Some popular EDI solution providers include:
– TrueCommerce
– SPS Commerce
– IBM Sterling
– GoAnywhere
When choosing an EDI provider, consider the following:
– Compatibility: Ensure the solution works with your existing accounting or ERP system.
– Scalability: Choose a platform that can grow with your business.
– Support: Make sure the provider offers excellent customer service and technical support.
2. Setting Up the Necessary Software and Systems
Once you’ve selected your EDI provider, the next step is to set up the necessary software and systems. This includes:
– Installing the EDI software: The software acts as a gateway to create, send, and receive EDI documents like invoices. Most EDI solutions have cloud-based options, so installation may be as simple as signing up and logging into the platform.
– Integrating with your accounting or ERP system: For EDI invoicing to be truly effective, it should integrate seamlessly with your existing business systems, like QuickBooks, SAP, or Oracle. This allows you to automatically generate invoices based on existing purchase orders or sales data, streamlining the entire process.
Tip:
Before integration, ensure you have backups of your current systems and data to avoid any potential issues during setup.
3. Mapping Invoice Data from Existing Systems to EDI Formats
Mapping data from your internal systems (like your ERP or accounting software) to the EDI format is one of the most crucial steps. EDI invoices need to follow a specific standardized format (such as EDI 810), which requires you to map fields from your current system to the corresponding EDI fields.
For example:
– Invoice number from your system will map to the EDI field that represents invoice identification.
– Item descriptions, quantities, and prices from your system will map to the respective EDI sections.
Most EDI platforms will offer a user-friendly interface that helps with this mapping process. However, if you’re unfamiliar with how EDI works, you might need support from the EDI provider or an EDI consultant to ensure everything is correctly aligned.
Tip:
Double-check the mapping process to ensure all the data is correctly transferred. Incorrect mapping could lead to errors in your invoices or delays in processing.
4. Testing the EDI Process Before Going Live
Before you start sending live invoices, it’s essential to test the EDI process. Most EDI providers offer a testing environment where you can simulate sending and receiving invoices without any risk to your actual data.
Testing allows you to:
– Check data accuracy: Ensure that the data in your invoices is correctly transmitted to the buyer’s system.
– Verify transmission success: Confirm that the invoice reaches the correct destination.
– Spot any issues early: Identify and correct any errors in the mapping or formatting.
During the testing phase, you may need to send test EDI 810 invoices to your trading partners to confirm everything works as expected. It’s better to resolve any issues during the test phase than to face problems once you start sending live invoices.
Tip:
Test with a variety of invoice scenarios to ensure that everything from simple invoices to more complex ones (with discounts, taxes, etc.) is handled correctly.
5. Troubleshooting Common Issues
Even after careful planning and testing, issues can still arise during the setup of EDI invoicing. Here are some common problems and troubleshooting tips:
– Incorrect Mapping: If your invoices aren’t being formatted correctly, revisit the data mapping process. Ensure that all fields are aligned with the correct EDI specifications.
– Transmission Failures: If the invoices aren’t being transmitted, check your internet connection, EDI service status, and integration settings. You might also need to confirm that both your and your trading partner’s systems are compatible with the same communication protocol.
– Data Integrity Issues: Sometimes, the data you enter might not match the buyer’s system requirements. Double-check the formatting, such as dates or numerical values, to ensure compatibility.
Most EDI providers offer detailed documentation and support to help resolve these issues quickly.
6. Resources to Help with the Transition to EDI Invoicing
Making the switch to EDI invoicing doesn’t have to be overwhelming. Here are a few resources to assist you in your transition:
– EDI Software Providers: As mentioned earlier, platforms like TrueCommerce and SPS Commerce offer robust support during the setup process.
– Online Communities: Forums like EDI-L or LinkedIn groups focused on EDI invoicing can offer advice and solutions to common problems.
– Consultants: If the process feels too complex, consider hiring an EDI consultant to guide you through the setup and integration process. This can be especially helpful for larger businesses or those with complex invoicing needs.
Creating an EDI invoice may seem like a daunting task, but by following the right steps, you can set up an automated invoicing system that saves time, reduces errors, and enhances efficiency. From choosing the right provider to testing the system and troubleshooting common issues, this process will set your business up for success in the world of digital invoicing. Don’t hesitate to take advantage of resources and support offered by EDI platforms to ensure a smooth transition. Once you’re up and running, EDI invoicing will become an invaluable tool for modernizing your invoicing processes.
6. Key Takeaways
To sum up, EDI 810 invoices are transforming the way businesses handle invoicing. By automating the process, companies can experience faster transactions, reduced errors, and significant cost savings. Throughout this article, we’ve discussed how EDI invoices simplify and streamline billing processes, making them a vital tool for modern businesses.
EDI invoicing improves efficiency by eliminating manual entry, saving time, and ensuring accuracy, all while reducing reliance on paper-based systems. It also offers transparency through easy tracking and reporting features, enhancing the relationship between businesses and their trading partners.
As you consider the future of your business, evaluating your current invoicing methods is essential. If you’re still relying on paper invoices or manual data entry, transitioning to EDI invoicing could be the key to improving efficiency, accuracy, and overall operational performance. EDI invoicing is no longer just for large corporations—small and medium-sized businesses can benefit from the automation and scalability that EDI offers.
Incorporating EDI invoicing into your processes can save you time and money, making your business operations smoother, more efficient, and more competitive. Consider evaluating EDI solutions to see how they can benefit your business in the long term.
7. Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is EDI invoicing suitable for small businesses?
Yes, EDI invoicing can be beneficial for businesses of all sizes, including small businesses. While EDI was once used primarily by large corporations, today’s cloud-based EDI solutions are scalable and affordable for smaller businesses. By automating invoicing, small businesses can reduce human errors, save time, and improve cash flow, just like larger companies.
2. What is the cost of implementing EDI?
The cost of implementing EDI invoicing varies depending on your business needs and the provider you choose. While initial setup costs may include software, training, and integration, many cloud-based EDI solutions offer subscription-based pricing that is more affordable. The long-term savings in terms of time, efficiency, and error reduction often offset these costs.
3. How secure is EDI invoicing?
EDI invoicing is highly secure. It uses encryption and secure protocols to protect sensitive financial data during transmission. The EDI network ensures that only authorized parties can send and receive invoices, minimizing the risk of fraud or data breaches. However, it’s important to choose a reputable EDI provider that offers strong security features.
4. Can I integrate EDI with my existing accounting software?
Yes, most modern EDI invoicing solutions can integrate seamlessly with popular accounting software, such as QuickBooks, SAP, or Oracle. This integration allows for a smooth flow of data from your accounting system to your EDI platform, ensuring that invoices are generated automatically based on your sales or purchase orders.
If you’re considering a transition to EDI invoicing, your provider can help with the integration process to ensure it works well with your existing systems.



